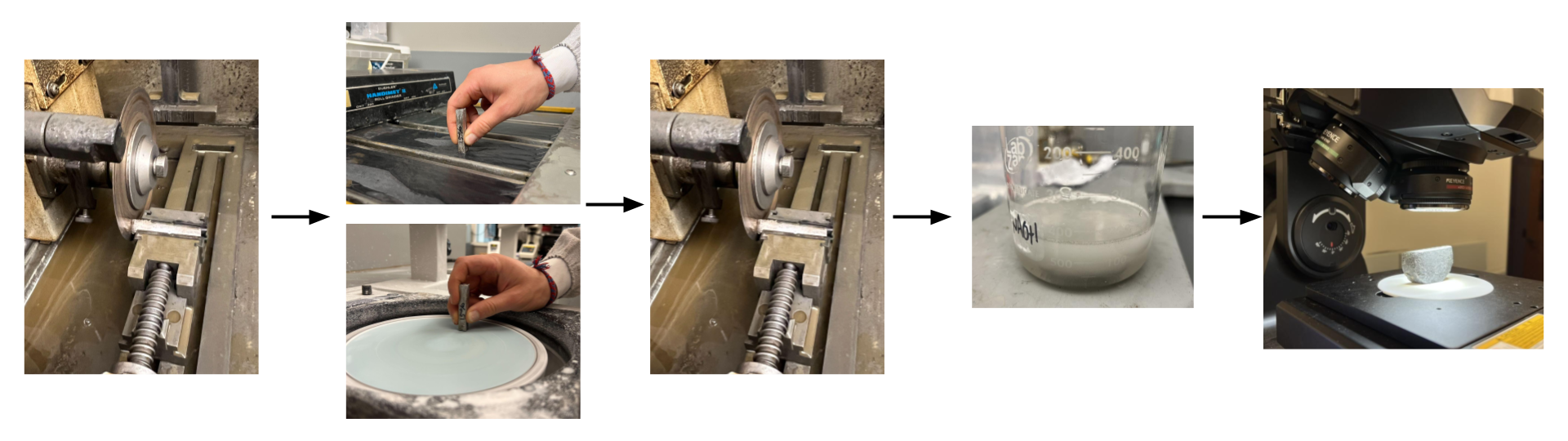
This project investigated how silicon composition and cooling rate affect the microstructure and hardness of sand-cast aluminum alloys near the eutectic composition (~12.6 wt% Si).
By systematically varying silicon content from 0–25 wt% and analyzing the resulting microstructures, we explored structure–property relationships central to alloy design and manufacturing.
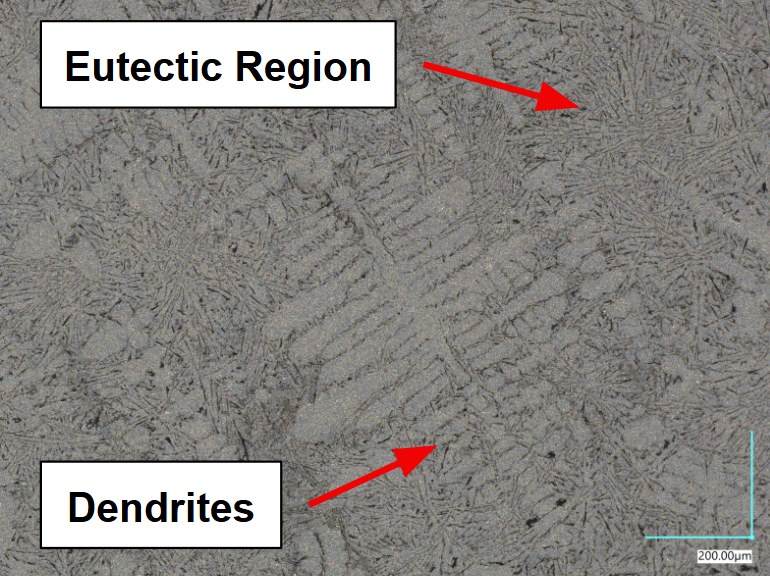
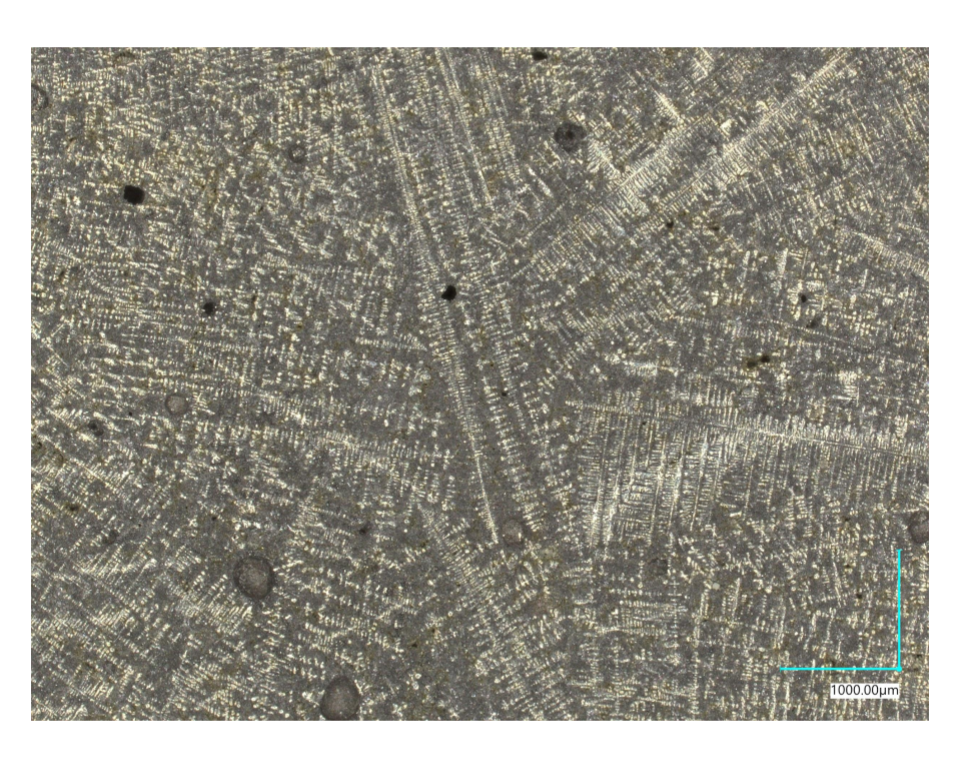


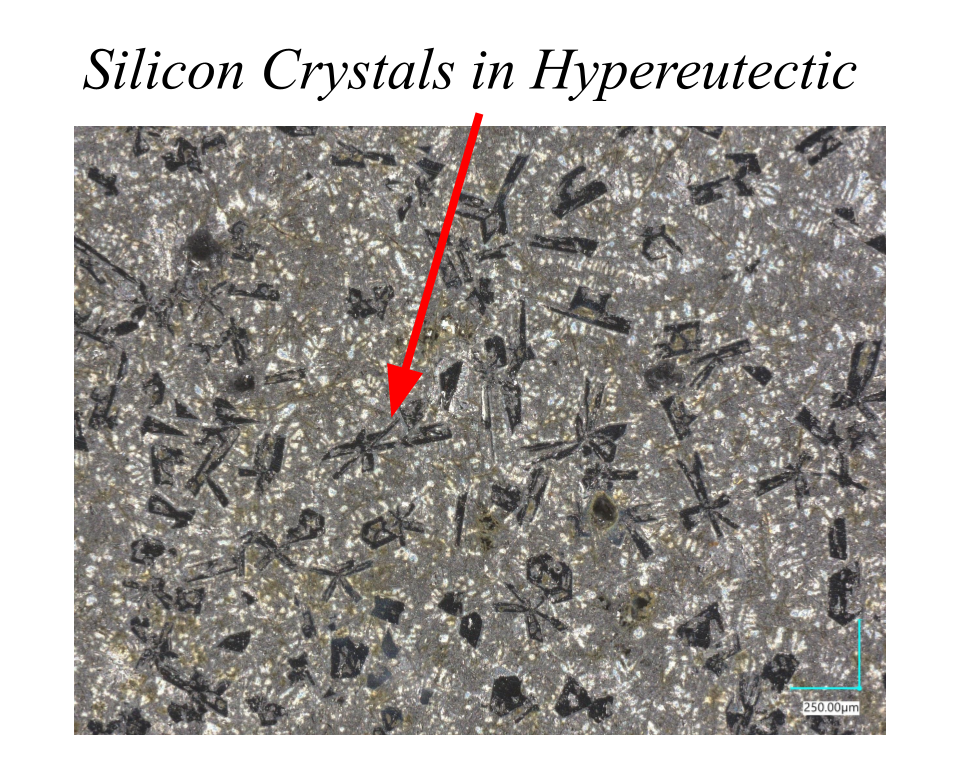

Fast Cooling
Dendrite-dominated structure
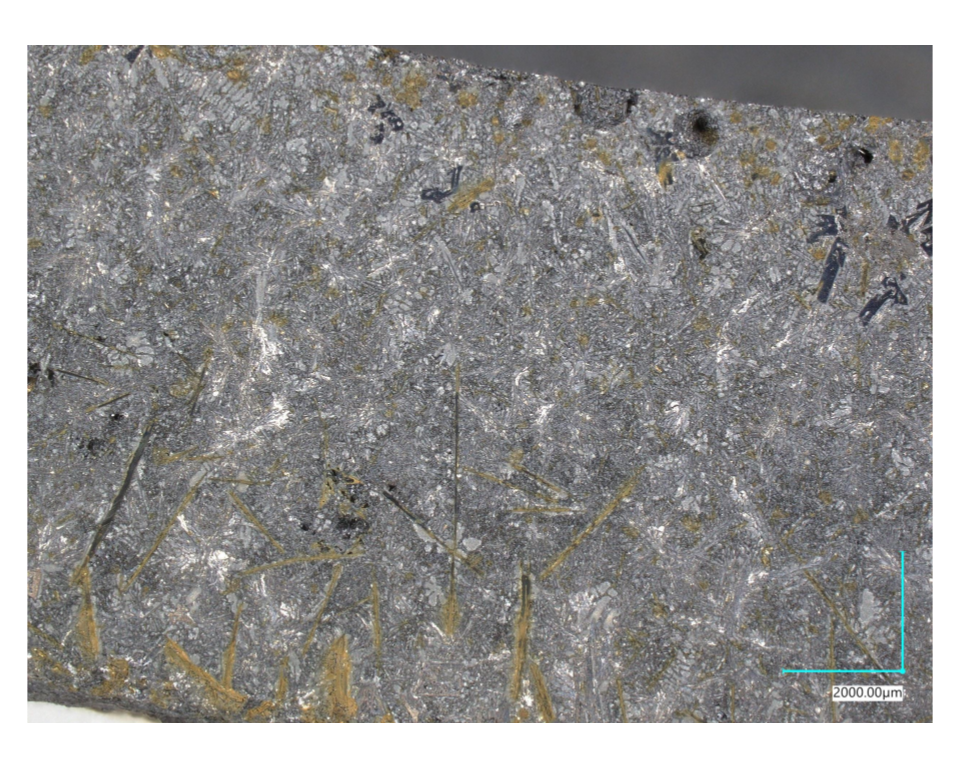
Slow Cooling
Eutectic-dominated structure
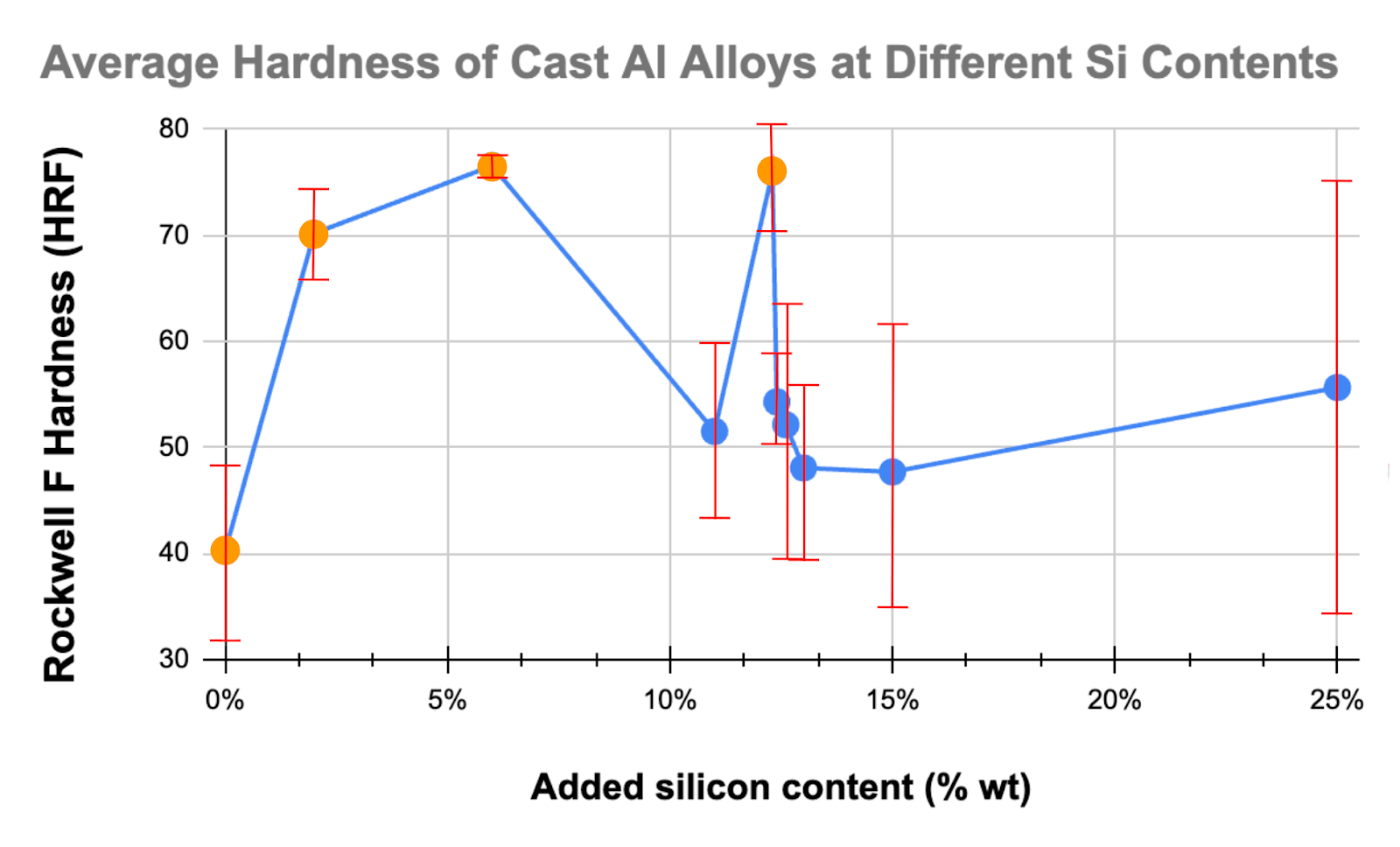
Hardness increased with silicon content up to the eutectic composition, where fine interwoven phases impede dislocation motion. At higher silicon levels, large primary Si crystals increased brittleness. (See Microstructure vs Silicon Content Effect of cooling rates.)